5 Ways To Improve Memory Skills in Students Who Struggle
As educators, we often wonder, Why do some students seem to retain information effortlessly while others struggle to recall what they learned just yesterday? How can I improve memory skills in students who struggle?
Improving memory skills in students is crucial for their academic success and overall learning. By applying specific techniques, educators can help students enhance their memory skills effectively.

The Neuroscience of Learning
The answer lies in the fascinating world of neuroscience, which sheds light on how memory works and how we can help students optimize their learning. Understanding the science of memory isn’t just an academic exercise—it’s a practical tool for creating effective learning environments.
The brain’s ability to form and strengthen neural connections plays a crucial role in memory retention, especially when it comes to complex subjects like math. When students actively engage with math problems, their brains create new pathways, making it easier to recall information in the future. Repetition, practice, and review are key to reinforcing these neural connections, as they encourage the brain to strengthen the synapses involved in memory.
To enhance memory skills in students, consider incorporating techniques such as storytelling, visual aids, and hands-on activities that make learning engaging and memorable.
Additionally, research shows that emotions and motivation can significantly impact memory. Positive emotions and a sense of achievement can enhance learning, while anxiety or stress may hinder it. By creating a supportive and motivating learning environment, students are more likely to form lasting memories of math concepts.

Our memory learning flash cards incorporate these principles by encouraging active learning techniques such as spaced repetition, visualization, and association. These strategies help students not only memorize formulas but also understand the underlying patterns in subjects like math, science, and language learning making it easier to apply them in different contexts. By tapping into the brain’s natural learning processes, students can improve both their memory and their overall mathematical abilities.
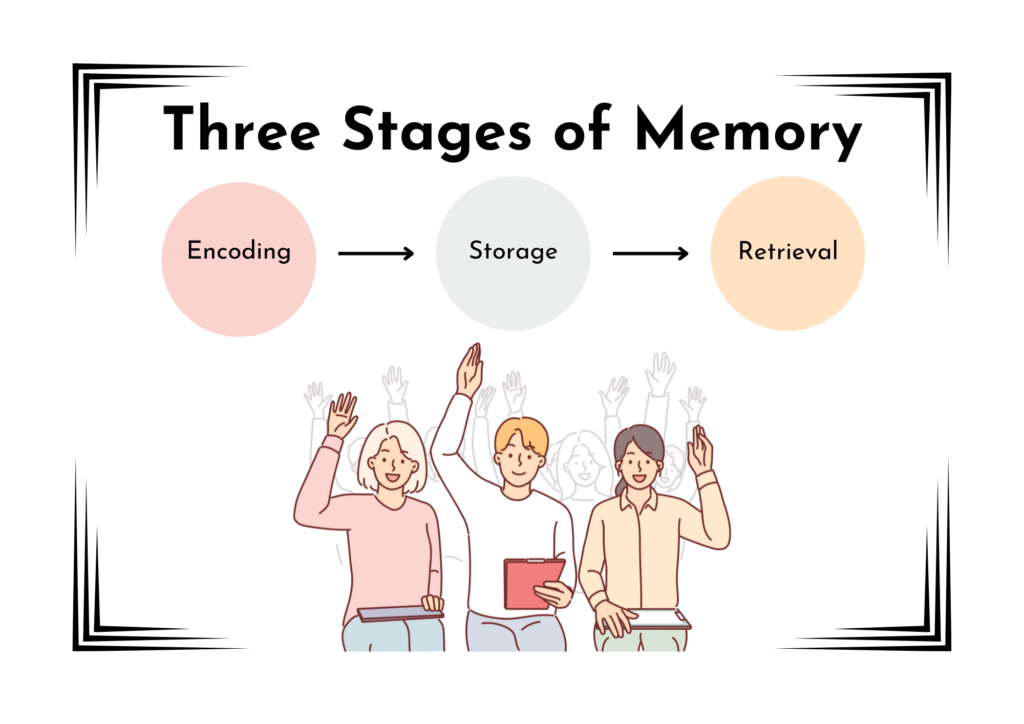
The Basics of Memory: Encoding, Storage, and Retrieval
Memory can be broken down into three key processes:
- Encoding: The process of taking in new information and converting it into a form the brain can store.
- Storage: Maintaining that information over time.
- Retrieval: Accessing the stored information when needed.
When students struggle to retain information, the issue often lies in one of these stages. For example, they might not have encoded the information deeply enough, or the retrieval cues might be weak.
How the Brain Stores Information
The brain uses two main types of memory for learning:
- Short-Term Memory (STM): This is like a temporary notepad where information is held for a few seconds or minutes. Think of it as the brain’s inbox.
- Long-Term Memory (LTM): For information to stick, it must move from STM to LTM, which involves a process called consolidation. Sleep, repetition, and meaningful connections all play a crucial role in this transfer.

Understanding the challenges students face in memory retention can help educators focus on improving memory skills in students through tailored strategies and support.
Why Do Students Forget?
Forgetting is a natural process and happens for several reasons:
- Decay: Without repetition, memories weaken over time.
- Interference: New information can overwrite or compete with older memories.
- Lack of Meaning: Information that feels irrelevant or disconnected is harder to retain.
Utilizing effective tools and resources, such as memory skills flashcards, can significantly enhance memory skills in students, making study sessions more productive.

Focusing on improving memory skills in students not only aids in their academic performance but also fosters a love for learning and intellectual curiosity.
Seven Tips to Help Improve Memory Skills in Students to Retain Information
Here’s where neuroscience meets practical teaching. By understanding how the brain works, we can employ strategies to help improve memory skills in students.
By incorporating physical activities that promote movement, we can further boost memory skills in students, leading to better concentration and retention.
1. Make Learning Meaningful
- The brain loves patterns and connections. When students can relate new information to something they already know, it sticks better.
- For example, in science, connect abstract concepts like photosynthesis to real-world examples, such as how plants in their garden grow.

2. Leverage Spaced Repetition
- Instead of cramming, encourage students to review material over several days. This strengthens neural pathways and improves long-term retention.
- Tools like flashcards or spaced repetition apps can help reinforce learning.
3. Engage Multiple Senses
- Multisensory learning—such as combining visuals, audio, and hands-on activities—activates more areas of the brain, making memories more robust.
- For example, using diagrams, videos, and experiments can make lessons more engaging and memorable.
4. Encourage Active Recall
- Rather than rereading notes, students should test themselves. Active recall strengthens retrieval pathways and boosts confidence in remembering.
- Practice quizzes or explaining concepts to a peer are great ways to use this technique.

5. Incorporate Movement
- Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, improving focus and memory. Short movement breaks during study sessions can enhance learning.
- Even a quick walk before a test can help students feel more alert and ready to recall information.

6. Prioritize Sleep
- Sleep is critical for memory consolidation. Encourage students to get enough rest, especially after learning new material.
- A tired brain struggles to encode and retrieve information effectively.
7. Emphasize the Power of Emotion
- Emotional experiences are remembered more vividly. Use storytelling, humor, or real-world scenarios to make lessons emotionally engaging.
What This Means for Educators and Parents
A collaborative learning environment can also enhance memory skills in students, allowing them to share strategies and learn from one another.
Understanding the neuroscience of memory can transform how we teach and support students. It’s not just about what they learn—it’s about how they learn. By focusing on strategies that align with how the brain works, we can help students retain information longer and apply it more effectively.

Lesson Plan: Building Memory Skills with Flash Cards
This engaging lesson plan uses flash cards to improve memory skills in middle school students, leveraging neuroscience principles like active recall, spaced repetition, and multisensory learning.
Objective:
Students will enhance their ability to encode, store, and retrieve information by creating and using flash cards to study a specific subject. Click on the subject material link to access some of our ready made flash cards to use in specific subjects.
Materials:
- Blank index cards or printable flash card templates
- Memory Skills Flashcards
- Markers, pens, or colored pencils
- A timer or stopwatch
- Subject material (e.g., vocabulary words, math formulas, science terms)
Lesson Steps:
- Introduction to Memory (10 minutes)
- Begin by explaining the three stages of memory: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Use relatable examples, such as remembering the lyrics of a favorite song.
- Discuss the tips to improving memory skills with the memory skills flashcards.
- Creating Flash Cards (15 minutes)
- Provide students with blank index cards or templates.
- Instruct them to write a question or term on one side of the card and the answer or explanation on the other. For example:
- Front: “What is the capital of France?”
- Back: “Paris.”
- Encourage creativity by using colors or drawings to make the cards visually engaging.
- Practice Active Recall (15 minutes)
- Split students into pairs or small groups.
- Have them quiz each other using the flash cards. Each student should try to answer the question before flipping the card.
- Incorporate Spaced Repetition (5 minutes)
- Explain how reviewing the cards over several days improves memory.
- Create a schedule for revisiting the cards: Day 1 (right after creating them), Day 3, Day 7, and so on.
- Memory Challenge Game (15 minutes)
- Organize a friendly competition.
- Divide the class into two teams. Take turns asking each team questions from the flash cards. Award points for correct answers.
- Encourage students to explain their reasoning for bonus points, reinforcing understanding.
- Reflection and Discussion (5 minutes)
- Ask students how they felt using the flash cards.
- Discuss which strategies helped them remember the information best.
- Reinforce the importance of practice and self-testing.
Ultimately, improving memory skills in students leads to lifelong learning benefits, giving them the tools to succeed academically and beyond.
Why Flash Cards Work
Flash cards engage multiple memory processes:
- Active Recall: Forcing the brain to retrieve information strengthens neural pathways.
- Spaced Repetition: Reviewing cards over time prevents forgetting.
- Multisensory Learning: Writing, reading, and discussing the cards activate different parts of the brain.
Final Thoughts
Memory is not just a talent—it’s a skill that can be developed. By using neuroscience-backed strategies, such as flash cards, we can empower students to take control of their learning and retain information more effectively. Whether you’re a teacher crafting lesson plans or a parent helping with homework, these techniques can make a world of difference.

With this lesson plan, middle schoolers will not only improve their memory but also develop study habits that will serve them well in the years to come. So grab some index cards and get started—learning has never been so much fun!
Related Topics
Connect to our other pages as you navigate our website.
- Back to School Resources Teachers Will Love
- 5 Ways to Promote Physical Health in Education
- Teacher Thoughts on Educational Policy
- The Simple Connection Between Laughter and Learning
- What Does ‘Student Identity’ in the Online Classroom Look Like?
- Six End of Year Summer Time Activities for Students
- 6 Amazing Science Resources for Teachers
- Math Oral Presentation Rubrics for Teachers
- ELA Oral Presentation Rubrics for the Classroom
- Presentation Rubrics and The Science Classroom
- Teaching the Art of Conversation to Middle School Students
Join Us Today!
Join us today to learn more about how to incorporate these resources into your classroom and support the mental health of your students.
Share Your Thoughts
Let us hear your thoughts on our approaches to help improve memory skills in students!







