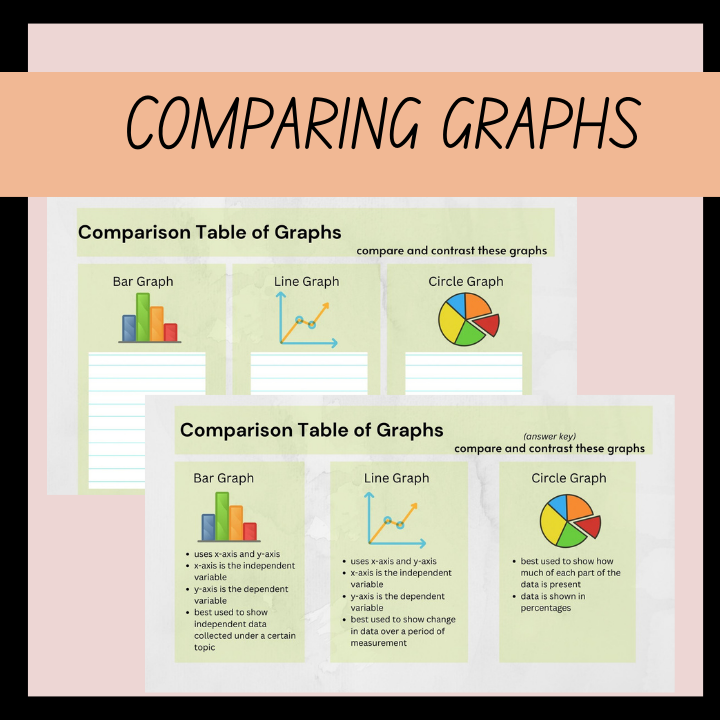
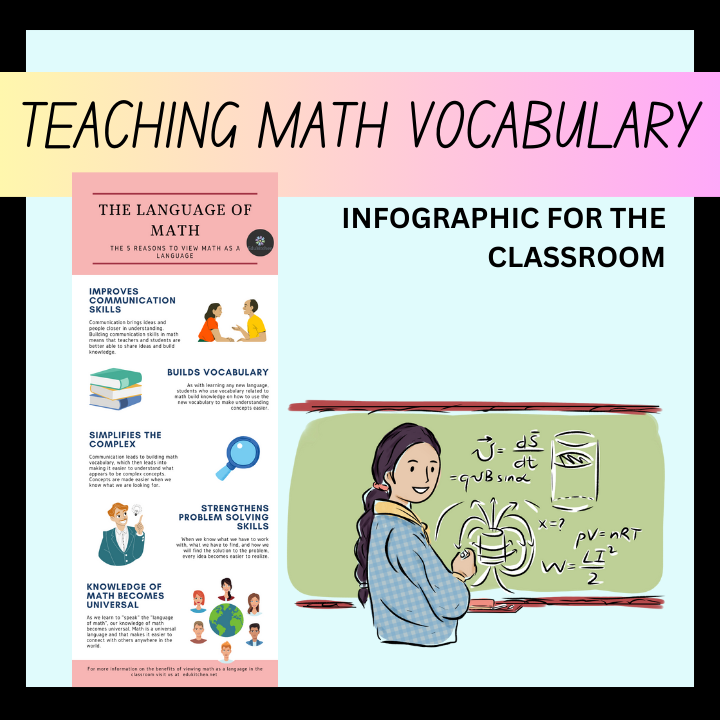
Math Learning
Explore our strategies in math lesson planning resources that help support teachers in planning out their lessons.
Use our proven math learning strategies for students designed for educators to help students excel in their mathematical journey and improve outcomes.
Our expertly crafted math learning strategies provide a comprehensive guide to help students excel in math at every level. From foundational skills to advanced problem-solving, these strategies make math accessible, engaging, and enjoyable for middle school and beyond. Perfect for teachers and parents looking to boost student confidence and understanding.
Check out our math related resources by clicking on the images below.
What is the Best Strategy to Teach Math?
By combining conceptual learning with confidence-building exercises, teachers can strike a balance between teaching math concepts and nurturing students’ confidence in learning math. These strategies involve incorporating real-world applications, interactive activities, and collaborative problem-solving to create a supportive and empowering learning environment.

Through targeted praise, constructive feedback, and personalized guidance, teachers can cultivate a growth mindset in students, encouraging them to embrace challenges and persevere in their mathematical journey. This holistic approach ensures that students not only develop a solid foundation in math but also gain the self-assurance to tackle complex mathematical concepts with confidence.
How Teachers Can Help Students Build Strategies in Math With Our Lesson Planning Resources
How can teachers help students develop their math learning?
Teaching math goes beyond solving equations and memorizing formulas. It’s about equipping students with learning strategies that help them approach problems confidently, think critically, and apply math in real-world situations. Our lesson planning resources help teachers show students how to build their strategies for math and include: posters, infographics, presentations, and worksheets. Click on the images below to learn more.
Explore our Resource Library
our library contains a variety of Math resources in the categories of posters, presentation guides, infographics, and student – centered worksheets
As teachers, we can help students develop a toolkit of strategies that will support their math learning across all levels. Below are effective methods to teach math learning strategies and enhance student success.
Gain Access to our Math Videos
Explore our collection of math videos, crafted to simplify complex topics and bring math to life for middle school students and beyond. These engaging and visually dynamic videos cover a wide range of concepts, from foundational skills to advanced problem-solving techniques. Perfect for classroom use or homeschooling, each video is designed to complement your lessons, making learning math both interactive and enjoyable. With clear explanations, real-world examples, and step-by-step guidance, our math videos are an invaluable tool for building confidence and mastery in mathematics.

Formative Assessments and Math
This video looks at how homeschooling teachers can use formative assessments in the math classroom

A Lesson on Adding Fractions
This video looks at a sample lesson to show how students can add fractions.

SEL in the Math Classroom
This video looks at how homeschooling teachers can use SEL in the math classroom.

Five Steps to Math Success
This video looks at five steps to math success in learning math outside the classroom.

How to Use Math Language
This video looks at using math vocabulary in learning like one would learn any spoken language.

A Lesson on Adding Integers
Access our wide range of math worksheets, infographics, presentations, and posters to use in your homeschooling classroom.
We’ve put together a list of key math learning strategies and descriptons as to guide math teachers with best practices when looking to help students improve on their approaches to learning math.
I. Encourage a Growth Mindset
The first step in teaching math learning strategies is fostering a growth mindset in students. Many learners feel defeated by challenging math problems and believe they “aren’t good at math.” By emphasizing that math abilities can be developed through effort and practice, you can shift their perspective from fixed ability to growth potential. Teach students to embrace mistakes as learning opportunities and encourage persistence, reinforcing the message that success comes from consistent effort.Rewind 10sPlayForward 10s
II. Use Visual Representations and Manipulatives
Math can be an abstract subject, and one way to help students understand abstract concepts is by using visual aids and manipulatives. Visual models like number lines, charts, graphs, and diagrams can help students see patterns and relationships between numbers. Manipulatives, such as blocks, fraction tiles, or counters, allow students to physically manipulate objects to better grasp concepts like addition, subtraction, and fractions. These tools bridge the gap between concrete and abstract thinking and provide students with another way to process and solve math problems.
III. Teach Problem-Solving Strategies
Problem-solving is the heart of math learning. Teaching students various strategies to tackle problems is essential for their mathematical development. Common strategies include:
- Breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Looking for patterns or relationships between numbers.
- Drawing diagrams or models to visualize the problem.
- Using estimation to check if an answer is reasonable.
- Working backward to solve equations or word problems.
Encourage students to verbalize their thought processes and explain how they approach different problems. This will help them internalize the steps and gain confidence in solving unfamiliar problems.
IV. Incorporate Real-World Applications
Math becomes more engaging and relevant when students can see its real-world applications. Relating math problems to everyday life helps students understand the importance of the subject. For example, use budgeting, shopping discounts, cooking measurements, or even sports statistics to demonstrate math concepts. This strategy not only increases student interest but also helps them apply math knowledge in practical situations outside the classroom.
V. Encourage Collaborative Learning
Collaboration allows students to learn from each other and share different problem-solving approaches. Group activities and math discussions promote critical thinking and communication, which are vital math learning strategies. By working together on tasks, students can clarify their own thinking, explore alternative strategies, and gain new perspectives. Peer teaching, where students explain concepts to one another, is also highly effective, as it reinforces the explainer’s understanding.

VI. Implement Metacognitive Strategies
Teaching students how to think about their thinking—also known as metacognition—can significantly improve their math performance. Encourage students to reflect on the strategies they use to solve problems and evaluate their effectiveness. Ask guiding questions like:
– “What steps did you take to solve this problem?”
– “Why did you choose this approach?”
– “What might you do differently next time?”

By becoming aware of their own thought processes, students can learn to adjust and refine their strategies for better outcomes.
VII. Teach Math Vocabulary
Understanding math-specific vocabulary is key to mastering mathematical concepts. Students often struggle with math problems not because they don’t understand the numbers, but because they’re confused by the language. Make sure to explicitly teach math terms, use them frequently in class, and encourage students to use them as well. Create word walls or glossaries to reinforce key terms like “equation,” “denominator,” or “variable.” Building a strong math vocabulary helps students comprehend problems more easily and increases their confidence.
VIII. Incorporate Spiral Review
Math concepts build on one another, so regular review is important to reinforce past learning. Spiral review involves revisiting previously learned concepts at intervals, integrating them into new lessons. This ensures students retain their knowledge over time and can apply old concepts in new contexts. Spiral review can be incorporated into daily warm-ups, homework, or assessments, keeping foundational skills sharp.
IX. Provide Timely Feedback
Giving immediate and constructive feedback is crucial for students to improve their math skills. Offer feedback that highlights what students did well and what they can improve. Be specific about their errors and provide guidance on how to correct them. Encouraging students to self-correct or rework problems helps them learn from their mistakes and reinforces the correct strategies.

X. Use Technology and Games
Incorporating technology into your math instruction can make learning more interactive and engaging. Math games, apps, and websites provide students with opportunities to practice math skills in a fun, competitive way. Adaptive learning tools, such as online platforms that adjust difficulty levels based on student performance, are also helpful in providing individualized practice. These tools can serve as a supplement to your teaching, offering students an alternative way to practice and reinforce skills.

Featured Math Resources
This page contains affiliate links to highlighted websites and/or resources. By clicking on the link and making a purchase we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Click here for full disclosure.
1. Subject Specific Worksheets
Engage students with a structured workbook focusing on key algebra concepts, perfect for practice and mastery.
2. Real-World Math Problem Pack
Explore math in the real world with problems inspired by everyday scenarios, from budgeting to travel planning.
3. Visual Math Aids Collection
This collection includes graphing templates, flowcharts, and step-by-step guides for visual learners.
Why Choose MyETIAcademy for Math Learning?
Our math resources are developed by education professionals to simplify lesson planning and support various learning styles. Each strategy is aligned with core math standards and designed to help students build confidence and expertise in math.
Get Started Today!
Explore our portfolio of images to find math resources that meet your students’ needs and bring math learning to life in your classroom.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective math learning strategies that educators can use to assist students?

Effective math learning strategies include using visual aids, incorporating technology, implementing collaborative learning, and providing real-world problem-solving scenarios, which can enhance understanding and retention of mathematical concepts.
How can students develop their own math learning strategies with the help of educators?
Educators can guide students in developing personalized math learning strategies by encouraging self-reflection on their learning styles, promoting goal-setting, and providing feedback that helps students identify and implement techniques that work best for them.
Why are math learning strategies important for student success in mathematics?

Math learning strategies are crucial for student success as they foster critical thinking, improve problem-solving skills, and enhance academic performance, enabling students to approach math with confidence and a deeper understanding of the subject.
What is an example of a strategy in math?
One effective strategy in math education is the “Think-Pair-Share” technique, a collaborative approach that helps students develop problem-solving skills, communication, and confidence in their understanding.
Here’s how it works:
Think: Students are first given a math problem to solve individually. During this time, they think through the steps, apply relevant strategies, and try to find a solution on their own. This encourages independent critical thinking and allows students to develop their own approach to solving the problem.
Pair: After working alone, students pair up with a partner to discuss their solutions. They explain their thought process and steps, compare their answers, and identify any differences. This phase allows students to learn from each other, clarify misunderstandings, and reinforce their reasoning.
Share: Finally, pairs share their solutions and reasoning with the entire class. This provides an opportunity to see multiple approaches to the same problem and fosters an inclusive environment where students learn from diverse perspectives.
The “Think-Pair-Share” strategy encourages active participation, strengthens conceptual understanding, and helps students articulate mathematical thinking—all of which are crucial for mastering math skills. This collaborative approach also makes math more interactive and engaging, making it an effective tool for educators to support deeper learning.
Related Topics
Explore more of our website to see what other topics we look to discuss.
- Discover My ETI Academy And Our Resources in Education
- Educational Courses for Teachers by the ETI Academy
- Free English Language Skills Resource
- Free Classroom Management Resource by the ETI Academy
- Subscribe to The ETI Academy Newsletters Today!
- Our Student Blogs Help to Motivate Students
- Middle School Teacher Blogs – My ETI Academy
- Educational Resources for New English Teachers
- Mental Health Topics for New Teachers in Education
- Why New Teachers Should Use These Online Learning Strategies
Join Our Math Based Newsletter

Our educational newsletters are designed to help students and parents in understanding changes in education and in reaching new levels of academic success with in dealing with the challenges in the classroom.
Contact Us Today
It has never been easier to create enthusiasm and confidence in your learning abilities with The ETI Academy.